Why a hip prosthesis luxates?
Statistically, a prosthetic head luxation occurs in 0.5-10% of cases (by different authors) after an initial hip replacement.
Published: 16.09.2022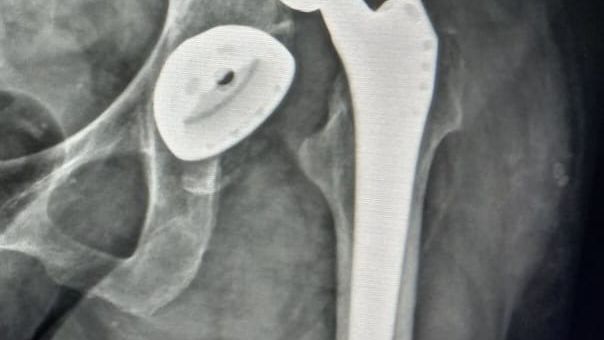
Why a hip prosthesis luxates?
Statistically, a prosthetic head luxation occurs in 0.5-10% of cases (by different authors) after an initial hip replacement.
Causes of the luxation:
Distorted balance of femur and gluteal muscles
Incorrect position of the prosthetic components
A patient’s failure to follow orthopedic and rehabilitation regimes
Symptoms of the luxation?
Usually, the luxation occurs suddenly. A frontal one - if a limb is rotated externally while lying down, a rear – if a patient was trying to make a deep squad to lean forward. At the moment of the luxation, a patient feels sharp pain and clicking in the joint. After this moment, a usual range of motion disappears, making the person unable to stand up and walk independently.
What should I do in a case of the luxation?
You should immediately seek medical aid. An orthopedic surgeon diagnoses a luxation of a joint basing on an X-ray image of the hip. Correction of the dislocation must be carried out by a professional and under general anesthesia. After this operation, it might be expedient to use a special orthesis for some period to restrict the motions of the joint.
When the luxation of the prosthesis requires surgical management?
- 1. When it is impossible to eliminate the dislocation in a “closed” manner.
- 2. When it is a repeated luxation of the prosthesis.
To choose the remedy for the luxation of your hip prosthesis, an orthopedic surgeon has to discover its background. During the operation, the surgeon could replace prosthetic head with a longer or bigger one, or turn the liner of the prosthesis with its cap towards the head luxation area. An ossificate remained in the acetabular cavity during the arthroplasty surgery could also lead to the luxation. Sometimes, it could be necessary to change the position of prosthetic cup and/or stem. For neurological or mentally ill patients unable to follow the orthopedic regime, double mobile systems are recommended because a smaller hear rotating in a bigger one is much less prone to the displacement.
May you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact me: +380989814929

- Tag:
- вивих ендопротезу кульшового суглоба
- ревізійне ендопротезування кульшового суглоба
- різкий біль та клацання у суглобі
- об’єм рухів у суглобі відсутній
- рентгенографія кульшового суглоба